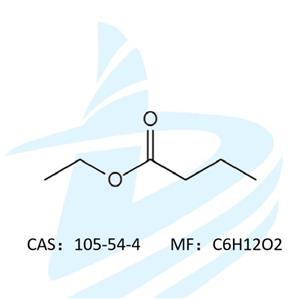
Physiological Function and Mechanism of Butyric Acid
1 improve digestive absorption function of the gastrointestinal tract Butyric acid can not only promote the development of gastrointestinal tissue but also increase the ratio of villi height to crypt depth (V/C). Cocoa stimulates the secretion of digestive fluid and improves the activity of digestive enzymes, thus increasing the digestibility of nutrients [2]. the mechanisms by which butyric acid promotes proliferation, differentiation, and maturation of gastrointestinal epithelial cells include direct energy supply to cells, regulation of neurohormones, stimulation of the release of gastrointestinal peptides or growth factors, regulation of intestinal mucosal blood flow, regulation of gene expression, and protein synthesis. 2 Regulating the balance of intestinal flora Research shows that Butyric acid can inhibit the proliferation or activity of harmful bacteria such as Salmonella, Escherichia coli, To promote the growth of lactic acid bacteria and other beneficial bacteria, It can also prevent necrotic enteritis induced by Clostridium perfringens. For the time being, The mechanism of butyric acid regulating intestinal flora includes the following four aspects. 1) reduce intestinal pH, Reduce the survival rate of pathogenic bacteria. 2) straight through the bacterial cell lipid membrane, Enter the bacteria and release the H, Denaturation of acid-sensitive proteins and DNA in bacteria, At the same time, in order to maintain pH neutral environment, Extra H, need to be pumped constantly The heaviest end results in bacterial energy depletion and death. 3) as a signal molecule, regulating host intestinal function by activating related signaling pathways, Maintain the balance of intestinal flora. 4) by inhibiting the activity of deacetylase (HDAC), promoting the expression of endogenous antimicrobial peptides in macrophages, and thus improve the antibacterial ability of macrophages. 3 Anti-diarrhea Diarrhea is one of the main diseases affecting animal health, causing slow growth of livestock and poultry and death of larvae. Studies have shown that butyric acid can promote the absorption of electrolytes and water, inhibit the release of secretin, and reduce the incidence of diarrhea. moreover, butyric acid activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ(ppar γ) or adenylate-activated protein kinase, promotes the expression of intercellular tight junction proteins, reduces cell permeability, and maintains intestinal mucosal integrity. thereby alleviating diarrhea caused by barrier failure, such as inflammatory bowel disease. 4 antioxidant function Oxidative stress is an imbalance between the oxidation reaction and the antioxidant system in the body. A large number of oxygen free radicals and DNA、 proteins react with oxidation, which leads to damage of animal tissue, an increase of compensation, obstruction of growth, and serious causes of various diseases. Studies have shown that butyric acid can increase the content of antioxidant glutathione and reduce the DNA injury induced by adverse factors by up-regulating the expression of catalase in order to alleviate the oxidative damage in animals. 5 anti-inflammatory effect Butyrate is a major energy source for colonic cells, Lack of butyrate or blocked butyrate metabolism can cause intestinal mucosal atrophy, Long-term deficiency can cause nutritional colitis. A lot of research shows, stimulation of intestinal butyric acid production through dietary fiber intake or direct supplementation of butyric acid may alleviate inflammatory conditions in patients with inflammatory diseases. Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of butyrate are as follows :1) down-regulate the expression of inflammatory factors, chemokines, inflammatory inducer enzymes, and adhesion molecules by inhibiting the activity of transcription factor-κB, Play anti-inflammatory effect; 2) reduce cell permeability by activating PPARγ, Maintain intestinal mucosal barrier function, Reducing the content of proinflammatory factors, In order to improve the body's anti-inflammatory ability; 3) as an HDAC inhibitor, Control of inflammation by promoting the secretion of antimicrobial peptides and T apoptosis; 4) activate G protein-coupled receptors, Regulating the expression of inflammatory-related factors, Inhibition of various adhesion molecules, chemokines and leukocyte migration, thereby alleviating the inflammatory response.